Category:Bioengineering: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Background == | |||
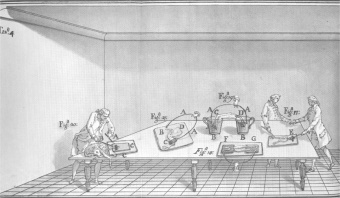
[[Image:Galvani-lab.jpg|thumb|right|340px|Luigi Galvani's laboratory]] | [[Image:Galvani-lab.jpg|thumb|right|340px|Luigi Galvani's laboratory]] | ||
Bioengineering is the practice of solving problems in the life sciences using an engineering approach. | |||
The design and production of medical devices—instruments engineered specifically to solve medical problems—go back thousands of years. This includes prosthetic devices, designed to replace missing body parts. Mummies with wooden digits have been found in Egyptian tombs. | |||
Luigi Galvani's experiments in the late 1700s led to the exploration of the link between electricity and animal physiology. This led to the study of using the electrical impulses of the body as diagnostic indications of health, such as in electrocardiology. | |||
Galvani’s student Alessandro Volta invented the first battery at the beginning of the 18th century, which almost immediately led to application of electricity to therapeutic purposes. The discovery by Wilhelm Roentgen of x-rays in the 19th century led to use of electromagnetic radiation for diagnostic purposes. | |||
The 20th century has led to many incredible discoveries and breakthroughs, especially regarding the convergence of mechanical, electrical and chemical engineering process into complex medical systems. Such systems included dialysis, the pacemaker and ultimately the artificial heart, prosthetic devices that could respond , and the DNA testing that underlies a range of genetic technologies. As we progress into the 21st century, bioengineering will continue to be an active area for technological breakthroughs and exciting new developments which have the potential to greatly improve the quality of life. | |||
== STARS Articles == | |||
IEEE STARS articles are peer-reviewed articles on the history of major developments in electrical and computer science and technology. Available in the bioengineering category are: | |||
*[[STARS:Electrocardiography|Electrocardiography]] | |||
*[[STARS:Pacemakers|Pacemakers]] | |||
== Subcategories == | == Subcategories == | ||
| Line 18: | Line 30: | ||
*'''[[:Category:Bioterrorism|Bioterrorism]]''' - Issues pertaining to biological devices and weapons used in a terrorist setting | *'''[[:Category:Bioterrorism|Bioterrorism]]''' - Issues pertaining to biological devices and weapons used in a terrorist setting | ||
*'''[[:Category:Computational biology|Computational biology]]''' - The development of data analysis and mathematics to study biological systems | *'''[[:Category:Computational biology|Computational biology]]''' - The development of data analysis and mathematics to study biological systems | ||
*'''[[:Category:Genetics|Genetics]]''' - The study of genes in living organisms | *'''[[:Category:Genetics|Genetics]]''' - The study of genes in living organisms | ||
Revision as of 13:01, 5 August 2014
Background
Bioengineering is the practice of solving problems in the life sciences using an engineering approach.
The design and production of medical devices—instruments engineered specifically to solve medical problems—go back thousands of years. This includes prosthetic devices, designed to replace missing body parts. Mummies with wooden digits have been found in Egyptian tombs.
Luigi Galvani's experiments in the late 1700s led to the exploration of the link between electricity and animal physiology. This led to the study of using the electrical impulses of the body as diagnostic indications of health, such as in electrocardiology. Galvani’s student Alessandro Volta invented the first battery at the beginning of the 18th century, which almost immediately led to application of electricity to therapeutic purposes. The discovery by Wilhelm Roentgen of x-rays in the 19th century led to use of electromagnetic radiation for diagnostic purposes.
The 20th century has led to many incredible discoveries and breakthroughs, especially regarding the convergence of mechanical, electrical and chemical engineering process into complex medical systems. Such systems included dialysis, the pacemaker and ultimately the artificial heart, prosthetic devices that could respond , and the DNA testing that underlies a range of genetic technologies. As we progress into the 21st century, bioengineering will continue to be an active area for technological breakthroughs and exciting new developments which have the potential to greatly improve the quality of life.
STARS Articles
IEEE STARS articles are peer-reviewed articles on the history of major developments in electrical and computer science and technology. Available in the bioengineering category are:
Subcategories
- Anatomy - Topics dealing with anatomy, the structure of living things
- Bioinformatics - The process of applying computer science and statistics to biology
- Biological topics - Various topics dealing with general biology including animals, microorganisms and vegetation
- Biomedical computing - Topics dealing with the application of computers in the biomedical field
- Biomedical engineering - Engineering specifically related to biomedical fields
- Biomedical equipment - Equipment used in a biomedical settings, such as biomedical electrodes, implants and surgical instruments
- Biomedical measurements - Measurements and monitoring instruments in the biomedical field
- Bioterrorism - Issues pertaining to biological devices and weapons used in a terrorist setting
- Computational biology - The development of data analysis and mathematics to study biological systems
- Genetics - The study of genes in living organisms
Subcategories
This category has the following 11 subcategories, out of 11 total.
Pages in category "Bioengineering"
The following 186 pages are in this category, out of 186 total.
A
- First-Hand:A Real First-Hand Account of the Startup Phase of Cetus
- Milestones:Active Shielding of Superconducting Magnets, 1984-1989
- Takuo Aoyagi
- First-Hand:Applying digital television technology to medical imaging = x-ray dosage reduction and non-invasive angiography
- Oral-History:Tatsuo Arai
- Oral-History:Robert Arzbaecher
- Oral-History:Eric Ash
- Archives:Automation for Health
- Roger E. Avery
B
- Oral-History:Albert "Les" Babb
- Oral-History:James J. Bailey and Rosalie Dunn
- Earl Bakken
- Oral-History:Earl Bakken
- Harrison H. Barrett
- Oral-History:James Bassingthwaighte
- Berger Publishes Paper on Electroencephalogram
- Oral-History:Gottfried Biegelmeier
- Archives:A Bio-Medical Engineering Career
- Otis Boykin
- Oral-History:Brad Nelson
- Thomas F. Budinger
- Building Blocks of Nanotechology
- Oral-History:Arthur Burks
C
- Oral-History:Norm Caplan
- Oral-History:Alicia Casals
- CAT, MRI, and Ultrasound
- Oral-History:Milton Chaffee
- First-Hand:Challenges IEEE Faced Supporting Ethical Behavior and Professionalism
- Oral-History:John C. Chato
- Oral-History:Shu Chien
- Oral-History:Clark Colton
- William Coolidge
- Rory A. Cooper
- Allan Cormack
- Oral-History:William E. Cory
- Walter B. Cozzens
- Imre Csiszar
D
E
- Oral-History:Murray Eden
- Willem Einthoven
- Electricity & Life
- Electrocardiography
- Electromagnetic Environmental Effects (E3)
- First-Hand:Electrophysiology and Defense, EKGs, Electroshock Therapy, and Antisubmarine Weaponry
- IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society History
- Oral-History:IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society Oral Histories
- Archives:New Applications of the Computer: Thelma Estrin and Biomedical Engineering
- Oral-History:Thelma Estrin (1992)
F
G
- Oral-History:Uzia Galil
- Luigi Galvani
- Leslie A. Geddes
- Oral-History:Leslie Geddes
- Oral-History:David Geselowitz
- John Heysham Gibbon
- Oral-History:Frank W. Godsey
- Harold S. Goldberg
- Oral-History:Alfred N. Goldsmith
- Oral-History:Martin Graham
- Oral-History:Robert M. Gray (1991)
- Oral-History:Robert M. Gray (1998)
- Oral-History:Wilson Greatbatch
H
- Oral-History:Abraham H. Haddad
- Archives:Papers of William Joseph Hammer
- Bin He
- Archives:Engineering in the Health Industry
- Julia F. Herrick
- Erwin Hochmair
- Ingeborg J. Hochmair
- Leroy Hood
- Oral-History:Ayanna Howard
- H. Malcolm Hudson
- Mark S. Humayun
- C. Warren Hurley
- Brian F. Hutton
- Hyperthermia: Microwaves as Cancer Treatment
J
K
L
M
P
R
- Biological Effects of Electromagnetic Radiation
- Nirmala (Nimmi) Ramanujam
- Oral-History:Buddy Ratner
- First-Hand:Re-Establishing IEEE Members' Right to Ethical Support in Employee-Employer Professional/Ethical Disputes
- Oral-History:Robert Rediker
- Oral-History:John M. Reid
- Rebecca Richards-Kortum
- Wilhelm Roentgen
- Charles Rosen
- Walter A. Rosenblith
- Robert Rushmer
S
- Oral-History:Murray Sachs
- Scanning Probe Microscopy
- Otto Schmitt
- Oral-History:Herman Schwan (1992)
- Oral-History:Herman Schwan (1999)
- Archives:Working to Establish a New Discipline: Herman P. Schwan and the Roots of Biomedical Engineering
- Nadrian Seeman
- Terrence Sejnowski
- Ascher Shapiro
- Lawrence A. Shepp
- Oral-History:Ralph M. Showers
- K. Kirk Shung
- Richard Skalak
- Oral-History:Allan Whitenack Snyder
- Samuel Thomas von Sömmerring
- Oral-History:John Staehlin
- First-Hand:Starting Up Cetus, the First Biotechnology Company - 1973 to 1982
- Oral-History:Karl Ulrich Stein
- Milestones:String Galvanometer, 1901-1905
- Takashi Sugiyama